What is dialysis?
Dialysis
Dialysis is the medical term for removing the waste and extra fluid from your blood that your kidneys can no longer remove themselves. When the waste is gone, you may feel better.
What is Peritoneal Dialysis (PD)?
Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) uses a special solution (dialysate) and your own peritoneal membrane - the lining of your abdomen - as the filter to help clean the blood and remove excess fluids. This method is like your regular kidney where fluid removal is continuous inside your body.

What is home hemodialysis (Home HD)?
Hemodialysis (HD) is a type of dialysis that filters your blood outside your body using a machine and a dialyser, which is a manufactured filter that acts like an artificial kidney.

What Is In-Center Hemodialysis (In-Center HD)?
Hemodialysis (HD) is a type of dialysis that filters your blood outside your body using a machine and a dialyser, which is a manufactured filter that acts like an artificial kidney.
Principles of dialysis
Dialysis removes the waste products and extra fluid from your blood by filtering them through a membrane/filter, similar to the way healthy kidneys would. During dialysis, blood is on one side of the membrane/filter and a special fluid called dialysate (containing water, electrolytes, and minerals) is on the other. Small waste products in your blood flow through the membrane/filter and into the dialysate.
The three principles that make dialysis work are diffusion, osmosis, and ultrafiltration.

Diffusion
During diffusion, particles in the areas of high concentration move towards the area of low concentration. Picture how a tea bag works - the leaves stay in the bag and the tea enters the hot water. In dialysis, waste in your blood moves towards dialysate, which is a drug solution that has none (or very little) waste. How much waste is removed depends on the size of the waste, the size of the pores (holes) in the membrane, what's in the dialysate, and like a tea, the length of treatment.1

Osmosis
During osmosis, fluid moves from areas of high water concentration to lower water concentration across a semi-permeable membrane until equilibrium is reached. In dialysis, excess fluid moves from blood to the dialysate through a membrane until the fluid level is the same between blood and dialysate.

Ultrafiltration
Ultrafiltration is the removal of fluid volume from a patient. In dialysis, ultrafiltration removes waste and excess fluids from the blood.2
What is peritoneal dialysis?

Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) uses a special solution (dialysate) and your own peritoneal membrane - the lining of your abdomen - as the filter to help clean the blood and remove excess fluids. This method is like your regular kidney where fluid removal is continuous inside your body.
A PD catheter is placed in the abdomen in surgery and is used to access the peritoneal membrane to allow for dialysis.
A special solution (dialysate, or dialysis solution) is placed in the abdomen through the PD catheter and is in contact with the peritoneal membrane. Waste in the blood and bodily fluids then pass through the peritoneal membrane, which acts as a natural filter for the solution.

Waste products and extra water in the blood are pulled into the solution by means of diffusion and osmosis. The used dialysis solution is then drained out through the PD catheter into a collection bag or other means of disposal. This process is called an exchange.
The small particles of waste float out of the blood, through the tiny holes in the peritoneum, the membrane lining the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities, and into the dialysis solution.
The waste particles float from the blood side where it is more crowded to the solution side that is less crowded.
The dialysis solutions that are used do several things: they help your body remove extra fluid, help with nutrition, replace some of the lost protein, and balance blood acid levels. Your doctor will determine your personal dialysis prescription (the right type of solution and number of exchanges) to meet your needs.
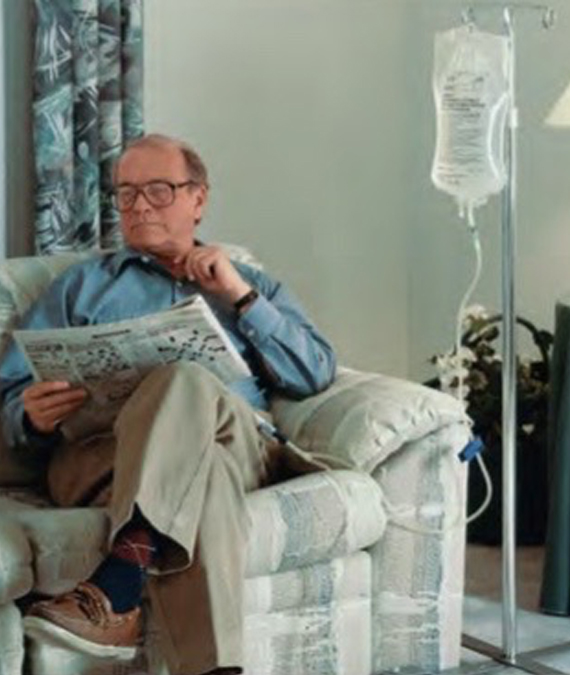

Peritoneal dialysis is done at home so that you have more flexibility to arrange your daily activities and schedule. You can even perform PD at work or on the road. This may allow you more time to enjoy your favorite things like travelling, school, work, hobbies, sports, visiting with friends and a full family life. You, your family members, or caregivers carry out the procedures for PD. Your healthcare team will train you and/or your caregiver on how to complete your treatments.
What is hemodialysis?
The word "hemo" refers to blood. Hemodialysis (HD) filters your blood outside your body using a machine and a manufactured filter, called a dialyzer. This dialyzer acts as an artificial kidney. The machine makes the dialysis solution, which is needed to remove excess water and waste from your blood.
During HD, a machine removes blood from your body using a needle or a central venous catheter. Your blood is then pumped through the dialyzer and cleaned. After this, the clean blood is returned to your body through a second needle or a second branch of catheter.
Hemodialysis is usually performed during a scheduled time at the hospital or in a dialysis clinic, and is referred to as in-center hemodialysis (ICHD). Most people require hemodialysis 3 times a week, with each treatment session lasting about 4 hours, depending on the dialysis prescription the doctor has recommended.
Please click here if you would like to read more detailed information about different types of dialysis and different ways of doing dialysis.